Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state (phase) that occurs without changing its temperature. The latent heat associated with melting a solid or freezing a liquid is called the heat of fusion; that associated with vaporizing a liquid or a solid or condensing a vapour is called the heat of vaporization. The latent heat is normally expressed as the amount of heat (in units of joules or calories) per mole or unit mass of the substance undergoing a change of state.
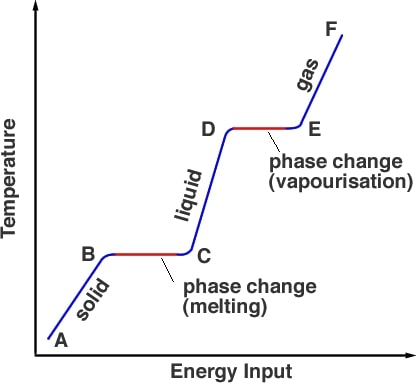
Latent heat is associated with processes other than changes among the solid, liquid, and vapour phases of a single substance. Many solids exist in different crystalline modifications, and the transitions between these generally involve absorption or evolution of latent heat. The process of dissolving one substance in another often involves heat; if the solution process is a strictly physical change, the heat is a latent heat. Sometimes, however, the process is accompanied by a chemical change, and part of the heat is that associated with the chemical reaction.
Heat of Melting: The amount of heat required to change a kilogram of substance from solid to liquid without change in temperature is called heat of melting.
𝑄𝑚𝑒𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 = - (𝑄𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑔 + 𝑄𝑤 + 𝑄𝑤) and 𝑄𝑚𝑒𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 = 𝑚𝑖. 𝐿𝑓
𝑄𝑚𝑒𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑛𝑔 = heat absorbed by ice as it melts to water.
𝑄𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑔 = 𝑚𝑖𝑐𝑤(𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇i), heat absorbed by ice as it warms from M.P.
𝑄𝑤 = 𝑚𝑖𝑐𝑤(𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇𝑤), heat loss of water.
𝑄𝑐 = 𝑚𝑐𝑐𝑐(𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇𝑤), heat lost by inner cup.
𝑐𝑤 = specific heat of water (1kcal/kg °C).
𝑐𝑐 = specific heat of calorimeter (0.09kcal/kg °C)
𝑇𝑖= initial temperature of ice.
𝑇𝑓 = final temperature of water mixture.
𝑇𝑤 = initial temperature of water.
Heat of Condensation: The amount of heat required to change a kilogram of substance from the gaseous to liquid state of matter at constant temperature is called heat of Condensation.
𝑄𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = - (𝑄𝑐𝑜𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑔 + 𝑄𝑤 + 𝑄𝑐) and 𝑄𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛= 𝑚𝑠. 𝐿𝑣/p>
𝑄𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑛𝑠𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = heat loss by steam while condensation.
𝑄𝑐𝑜𝑜𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑔 = 𝑚𝑠𝑐𝑤(𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇𝑠), heat loss by steam while condensation.
𝑄𝑤 = 𝑚𝑤𝑐𝑤(𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇𝑤), heat gained by water.
𝑄𝑐 = 𝑚𝑐𝑐𝑐(𝑇𝑓 − 𝑇𝑤), heat gained by calorimeter cup.
𝑇𝑠 = initial temperature of steam.