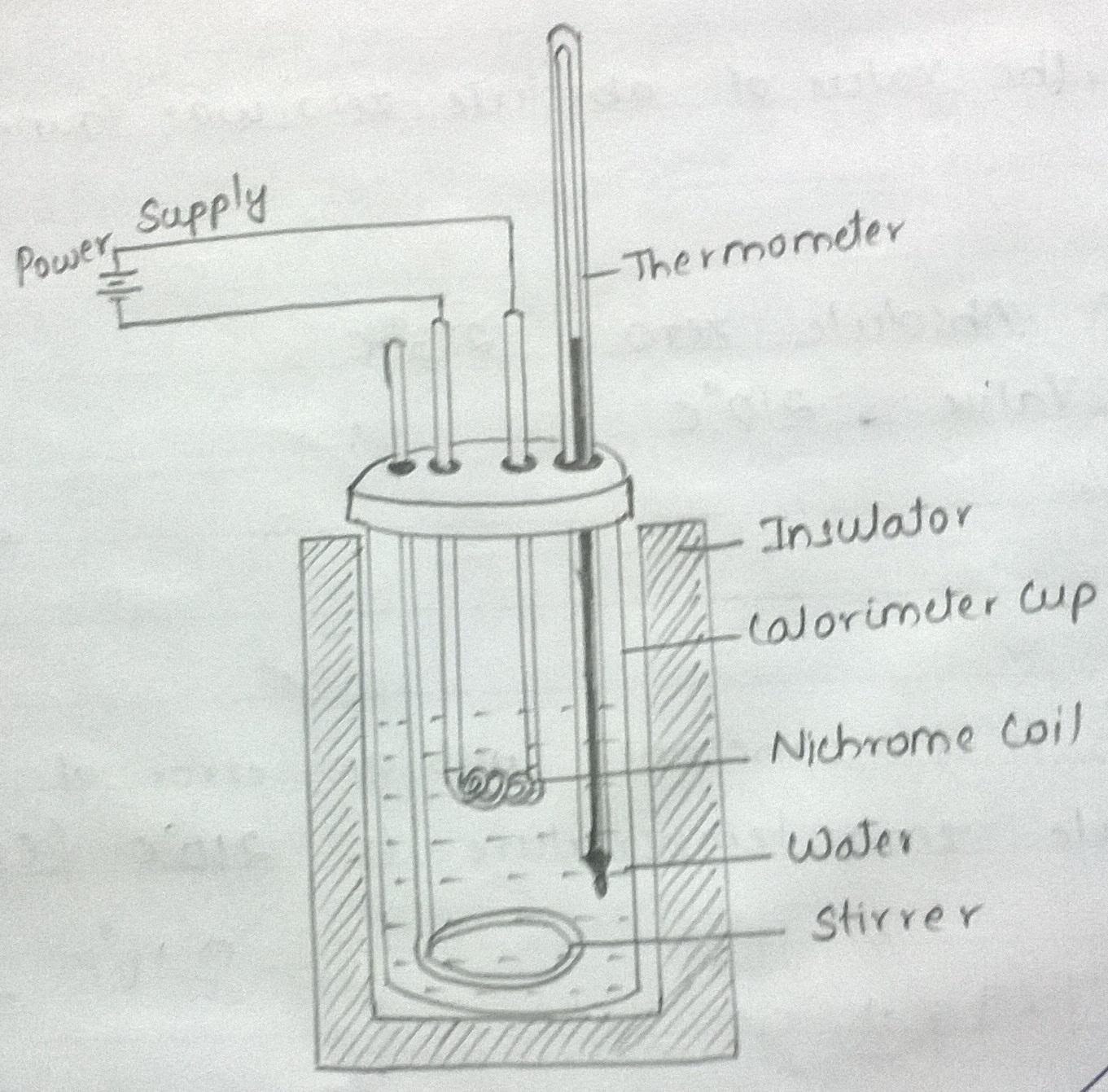
A Fixed volume of water taken in a calorimeter cup (both at room temperature), is heated by passing a constant current through the immersed nichrome wire maintained at a constant voltage across it.
Make the following table in your notebook and fill in the details.
|
S.No |
Physical quantity |
Independent / Dependent |
Measured with |
Measuring instrument’s |
||
|
Minimum |
Maximum |
Least count |
||||
|
1 |
Temperature |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
Time |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
Mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
Voltage |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
-
Connect the circuit.
-
Measure the mass of the calorimeter cup + stirrer. Let this be \(m_{1}\) grams.
-
Pour water into the cup so that Nichrome resistor coil is covered by about an inch of water.
-
Now, measure the mass of the calorimeter + stirrer + water. Let this be \(m_{2}\) grams.
-
Insert a thermometer into the water in the calorimeter, taking care to see that the thermometer bulb is not in contact with nichrome coil.
-
Measure the initial temperature (\(T_{1}\)) after allowing a couple of minutes to allow the thermometer bulb to attain equilibrium with the water in the calorimeter.
-
Turn on the power supply and simultaneously turn on the stop watch.
-
Quickly adjust the voltage to get a current of about one ampere in the circuit as read by the current meter of the power supply unit. Note down the current as I amps. Turn the V/I switch on the power supply unit to read the voltage. Let this be V volts. Keep gently stirring the contents of the calorimeter taking care to see that the stirrer does not come in contact with the nichrome coil in the calorimeter. A contact is indicated by a sudden change in voltage or by squeaking sound from the power supply unit.
-
Note down the temperature at regular intervals.
\(m_{1}\)= _________ gm \(T_{1}\) = _________
\(m_{2}\)= _________ gm \(T_{2}\) = _________
\(I\) = _________ amp \(T_{3}\) = _________
\(V\) = _________ volts
Table III : Measurements. Heating
Cooling
Temperature (℃)
Time (s)
Temperature (℃)
Time (s)
- Record the values of temperature as a function of time in a table.
- When the temperature of the calorimeter contents reaches about 10 to 20 degrees Celsius higher than the starting temperature turn off the power supply. Call this time as t. Note this temperature as \(T_{2}\).
- Continue making observations of temperature at regular intervals until another t/2. Note the temperature at this time as \(T_{3}\).
-
Plot the following graphs
- Temperature vs. Time for heating
- Temperature vs. Time for cooling
-
Calculate the Mechanical equivalent of heat as follows–
By Radiation Correction $$T_{2}'=T_{2}+T_{2}-T_{3}$$ Mechanical Equivalent Of Heat $$1\hspace{0.5cm}J= \frac{VIt}{(m_c.s_c+m_w.s_w)(T_{2}'-T_{1})} cal$$ - Perform the least square fitting of the data in graph A to a straight line.
- Perform the least square fitting of the data in graph B to a exponential decay. The same graph can be plotted as \(ln(t)\) vs. Temperature and fit then fit to a straight line.